Tobramycin is an antibiotic used most commonly in cats for eye infections. In this article, you will learn more specifically about the tobramycin ophthalmic ointment and solution, potential side effects to watch for, and some of the most frequently asked questions.
Tobramycin for Cats Overview

About Tobramycin for Cats
Tobramycin drops are commonly used for bacterial eye infections.
Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Aminoglycosides are considered bactericidal and their efficacy is dependent on the concentration of antibiotic present.
Like other aminoglycosides, the spectrum of bacteria that tobramycin is effective against includes: E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, Enterobacter, Mycoplasma, and Staphylococcus, among others.
Tobramycin does exist in a parenteral or injectable form. However, it is rarely used except in cases where bacterial infections are resistant to more commonly used aminoglycosides, and is only used in a hospital setting.
The more commonly used form of tobramycin as a prescription drug is an ophthalmic preparation, which is used for treating bacterial eye infections on the surface of the eye.
The tobramycin itself kills bacteria by actively being transported inside the bacteria and binding to a special receptor that leads to interference with the bacteria’s protein synthesis. This assists in causing bacterial death.
Also Read: Bacterial Infections In Cats: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
What Tobramycin Does
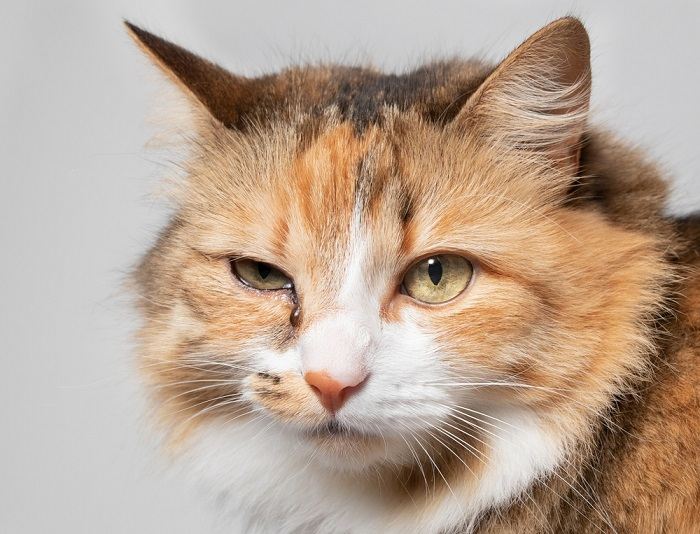

Heavy discharge in the eye can indicate a bacterial infection.
Tobramycin ophthalmic ointment or solution may be commonly used in cats experiencing an upper respiratory infection or conjunctivitis where noticeable swelling of the eye, eyelids, and/or discharge is present.
Like all antibiotics, tobramycin is only effective against bacteria and not as an antiviral or for use against fungal organisms. Because viruses, like feline herpes virus, are common causes of upper respiratory signs and conjunctivitis in cats, it is important for your veterinarian to determine if bacterial involvement is likely.
Heavier mucoid, yellow, or green discharge can be an indication of bacterial involvement. Your veterinarian may wish to collect samples for a cytology to look at under the microscope, or a culture, to determine how to proceed.
Another situation where antibiotic drops like tobramycin are often used is in the case of a scratch or ulcer on the eye. In cats, this is most often due to an injury sustained by another cat. An initial scratch may develop into an ulcer if it gets infected by bacteria.
It is important to make a distinction between typical bacterial ulcers and herpetic ulcers of the eye, which are caused by feline herpesvirus. Viral ulcers cannot be treated with tobramycin and require different treatment. Your veterinarian can help determine the distinction.
Also Read: Cat Eye Infections: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
Dosing Tobramycin for Cats
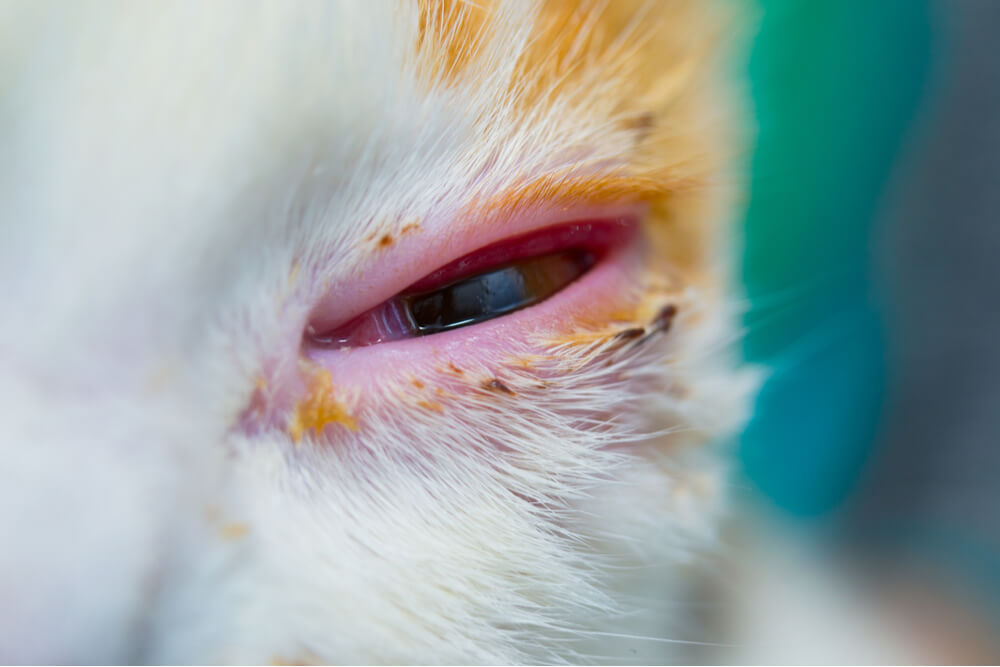
Watch closely for any adverse effects from applying Tobramycin to your cat.
The most common adverse effects of tobramycin include burning and irritation upon application. The conjunctival tissues of the eye and lids may also become red, inflamed, or irritated if a pet is sensitive to tobramycin.
When used systemically in cats, any aminoglycoside, like tobramycin, can cause toxicity to the kidneys and inner ear. Cats can be more susceptible to these effects.
Although ophthalmic tobramycin is not a systemic drug and such effects from an ocular preparation would be rare, it is still recommended to monitor for signs like decreased appetite, lethargy, excessive drinking and urination, vomiting, and balance and coordination issues.
Also Read: 10 Subtle Signs Your Cat May Be Sick
Dosing Tobramycin for Cats
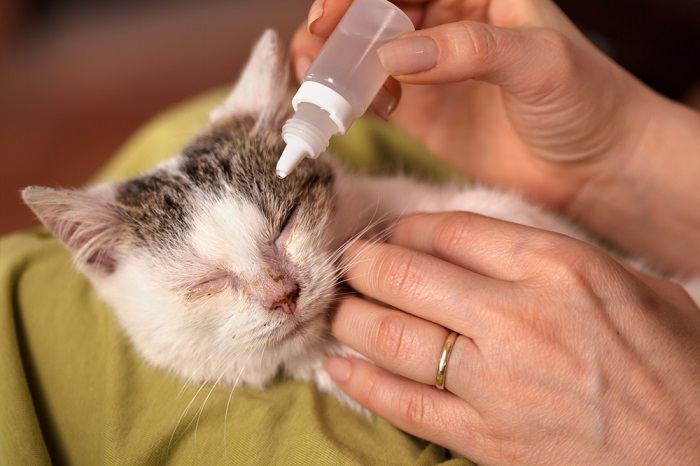
Be gentle when using dropper bottles around your cat’s delicate eyes.
For the tobramycin ophthalmic antibiotic eye drops, common dose recommendations are 1-2 drops in the affected eye. If using an ointment, you generally want a ¼-½ inch strip (about ½ to 1cm) across the surface of the eye.
When applying eye medication, always be careful to apply the drop or ointment without contacting the external eye surface of the cornea with the tube or dropper bottle, as this could further irritate the eye surface.
The frequency is typically at the minimum every 12 hours, but in some cases, your veterinarian may recommend giving the drops four to six times a day or more. Always clarify with your vet how frequently the drops should be given for your cat’s condition.
If your cat is getting any other ocular medications, it is best to use solutions before ointments and to separate medications out by at least 5 minutes.
Eye medications will also be more effective with as little discharge on the surface of the eye as possible. Using a warm damp washcloth, you can provide additional eye care by gently blotting or wiping any discharge from the eyelids. Do not try to wipe the surface of the eye itself, as this can cause keratitis or further irritation of the corneal surface.
Also Read: The 7 Best Cat Wipes For Dander And Dirt
Conclusion

Tobramycin is most commonly used as an ophthalmic drop for infections affecting the eye. Injectable tobramycin is rarely used except in select cases. While most cats will have no problem with tobramycin eye drops, always be aware that cats can have increased sensitivities to this antibiotic class, and monitor your cat for any concerns after starting use.
Drug Dosing Disclaimer: We are only able to provide doses for medications that are FDA approved for use in cats and only as the label guidelines dictate. For medications that are used off-label we can only provide guidelines and safety information for use. Safe and appropriate dosing for off-label medications can only be determined by a primary care veterinarian.
We encourage you to work with your veterinarian to determine if a particular medication is appropriate for your cat. Changing or adjusting a dose for your cat on your own without consulting with a veterinarian can carry risk. We do not encourage use of medications prescribed for human use in pets without first consulting with a primary care veterinarian.