Bacteria are everywhere!
Most bacteria are harmless to both us and our cats, and many are actually beneficial. However, some types of bacteria (called pathogenic bacteria) can make our cats unwell if their immune systems are unable to fight them off.
Bacterial infections are a common cause of illness in cats, but luckily most bacterial infections can be treated.
How Do Cats Get Bacterial Infections?
Bacteria, or germs, are microscopic organisms that are the size of just one cell. Bacteria play a vital role both inside our bodies, and in the world around us.
Like us, our cats are exposed to thousands of bacteria every day, and most of these don’t make them sick. However, if your cat encounters a harmful or pathogenic bacteria, they can multiply within your cat’s body resulting in a bacterial infection.
Symptoms of Bacterial Infection in Cats
Bacterial infections can affect any part of your cat’s body, and the symptoms they cause depend on the type of bacteria and the area of your cat’s body that is affected.
Common clinical signs of a bacterial infection include:
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Eating less
- Weight loss
- A bad smell
Other signs tend to be more specific to the area of the body that is affected. Common bacterial infections in cats include:
Respiratory Tract Infections
Respiratory tract infections in cats often cause sneezing, runny eyes (conjunctivitis) and nose, changes in breathing, or a cough.
Gastrointestinal Infections
Infections of the gastrointestinal system in cats often cause vomiting and diarrhea, as well as reduced appetite and weight loss.
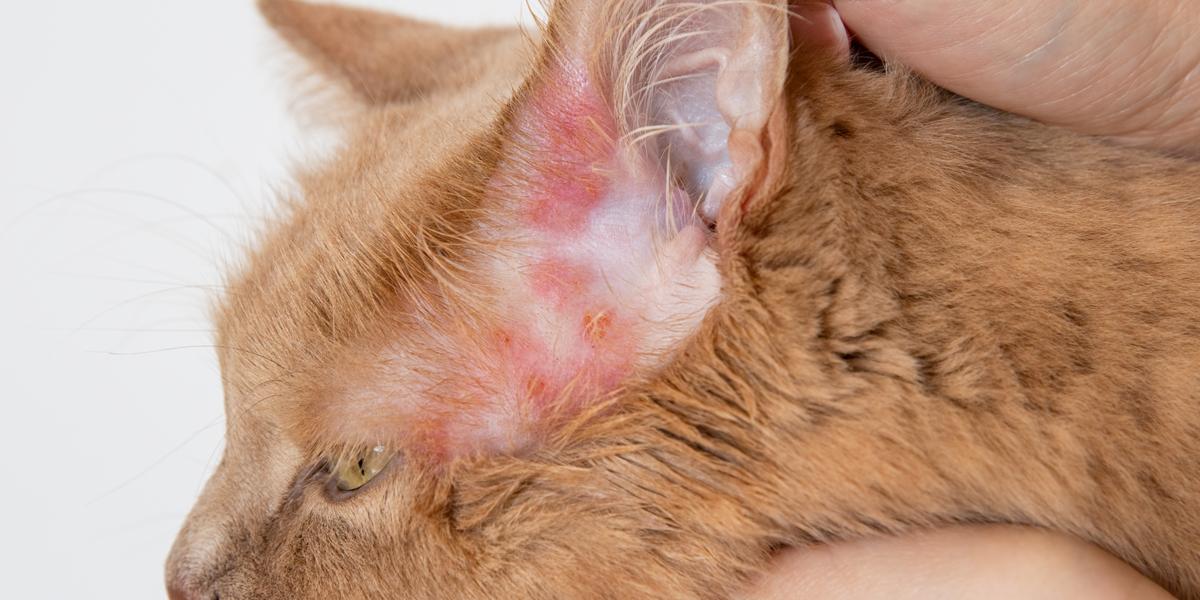
Ear and Skin Infections
Skin disease and ear infections are another common bacterial infection seen in cats. Signs include redness of the skin, scaly skin, a bad smell, itching, hair loss, pus, and lesions such as scabs, spots, abscesses, or wounds.
Dental Infections
Cats commonly suffer from infections in their mouths, particularly if they have had untreated dental disease for some time. Signs of a tooth infection include going off their food, pain when eating or opening their mouths, bad breath, or pus coming out of the mouth.
Urinary Tract Infections
Lower urinary tract infections such as bladder infections (also called cystitis) in cats may cause frequent urination in unusual places, blood in the urine, and pain when urinating, which may cause your cat to cry out.
It is important to note however that in cats under the age of 10, most cases of cystitis are not caused by infection and therefore do not need treatment with antibiotics.
Uncommon Bacterial Infections in Cats

Cat sneezing occurs for a wide variety of reasons, including viruses, infection, irritation, and more. But how do you know why your cat is sneezing?
All your cat’s organs can be affected by bacterial infections. We have listed the symptoms of the most common types of bacterial infections in cats above. However, your cat could also suffer from bacterial infections of the blood, immune system, bones and joints, and other organs such as the heart and brain. These infections can be very serious but are uncommon.
What Causes Bacterial Infections in Cats?
Bacterial infections can occur in healthy cats of any age, as your cat encounters thousands of bacteria every day. Most of these bacteria are harmless, and your cat’s immune system will protect them from many of those that can cause disease. However, sometimes a harmful bacteria will break through your cat’s immune defenses and cause an infection.
Common sources of infection include contaminated food (particularly raw meat) or water, or contact with another infected cat.
Bacterial infections are more likely to affect cats with weakened immune systems. This includes older cats and those who already have other illnesses, particularly feline leukaemia virus (FeLV) or feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV). These cats are less able to fight off infection, and so more vulnerable to becoming ill.
What Are the Types of Bacterial Infections in Cats?
Some of the common types of bacteria that can cause illness in cats include:
- Campylobacter
- E. coli
- Salmonella
- Staphylococcus
- Streptococcus
- Toxoplasmosis
However, not all strains of these bacteria always cause disease in healthy adult cats.
How Do You Diagnose Bacterial Infections in Cats?
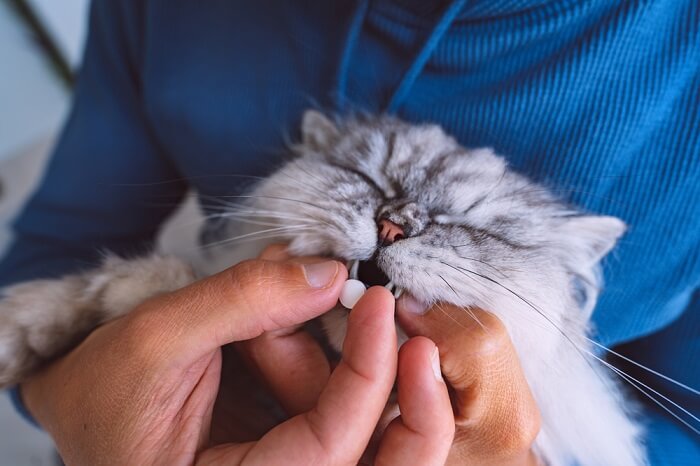

Some cats with bacterial infections may need to take oral antibiotics to combat the infection.
If you suspect your cat might have an infection, it is important to take them to see your veterinarian. Sometimes, your veterinarian may suspect a bacterial infection from their physical examination or history.
However, a bacterial infection generally cannot be confirmed without taking a sample and examining it under the microscope where the bacteria themselves can be seen. Your veterinarian may take a swab of the skin or ear, a sample of joint fluid from a suspected infected joint, or a sample of the feces if your cat is showing signs of a gastrointestinal infection.
To work out the type of bacteria present, and the right type of antibiotic to treat it, this sample will need to be sent to a laboratory for culture and sensitivity testing. This is where the sample is kept in conditions that enable the bacteria to grow and the type be identified, and different antibiotics are tried to see if they are effective at killing the bacteria.
How Do You Treat Bacterial Infections in Cats?
Infections with pathogenic (harmful) bacteria are treated with antibacterial treatments. Many infections will require treatment with antibiotics, usually tablets. However, local infections, such as skin, ear, or eye infections, may be treated with topical treatments, such as antibiotic or antibacterial ointments that are applied only to the affected area.
Over the last few years, we are seeing that bacteria are becoming more resistant to antibiotics, meaning that some types of infections are becoming difficult to treat. Antibiotic resistance is very dangerous for humans and animals, and therefore it is vital that antibiotics are only used when absolutely necessary, and that we use the right antibiotics when we do use them.
If your cat is prescribed antibiotics, make sure you use them exactly as your veterinarian has described and ensure you attend follow-up appointments. This will help reduce the development of antibiotic resistance which is vital for future cat health.
Remember, viral infections cannot be treated with antibiotics.
Are There Home Remedies for Bacterial Infection in Cats
If you suspect that your cat has a bacterial infection, it’s crucial to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Bacterial infections in cats often require prescription antibiotics, and home remedies are not sufficient on their own in case your cat suffers from a bacterial infection.
How Do Cats Recover From Bacterial Infections?
How well cats recover from bacterial infections depends on their immune system, the type of bacteria, the area of the body that is infected, and whether the bacteria are resistant to the type of treatment used.
The good news is most simple and common infections in healthy adult cats are currently easily treated with antibacterial treatments.







