Why use a cat stool chart? Because your cat’s feces is one of the biggest indicators of their health.
Put simply, a healthy cat should have healthy stools. While there are many specific health issues that can cause signs from constipation to diarrhea, it’s a simple rule that normal feces (or stools) are a good sign that your cat is thriving.
When you visit your veterinarian, it’s likely that you will be asked to describe your cat’s stools, as part of the general gathering of information about your cat’s health, and in particular, information about the gastrointestinal tract.
Cat Stool Chart
The cat stool chart infographic below is a simple, clear way of giving you information to help you decode the appearance of your cat’s feces.
The image on the left-hand column is the starting point: choose whichever one most closely resembles your cat’s stool. The second column is a written description of the appearance of the stool, and the third column is an explanation of the most likely reason for that appearance. Finally, the fourth column gives you advice on what action you need to take as a consequence of that particular stool appearance.
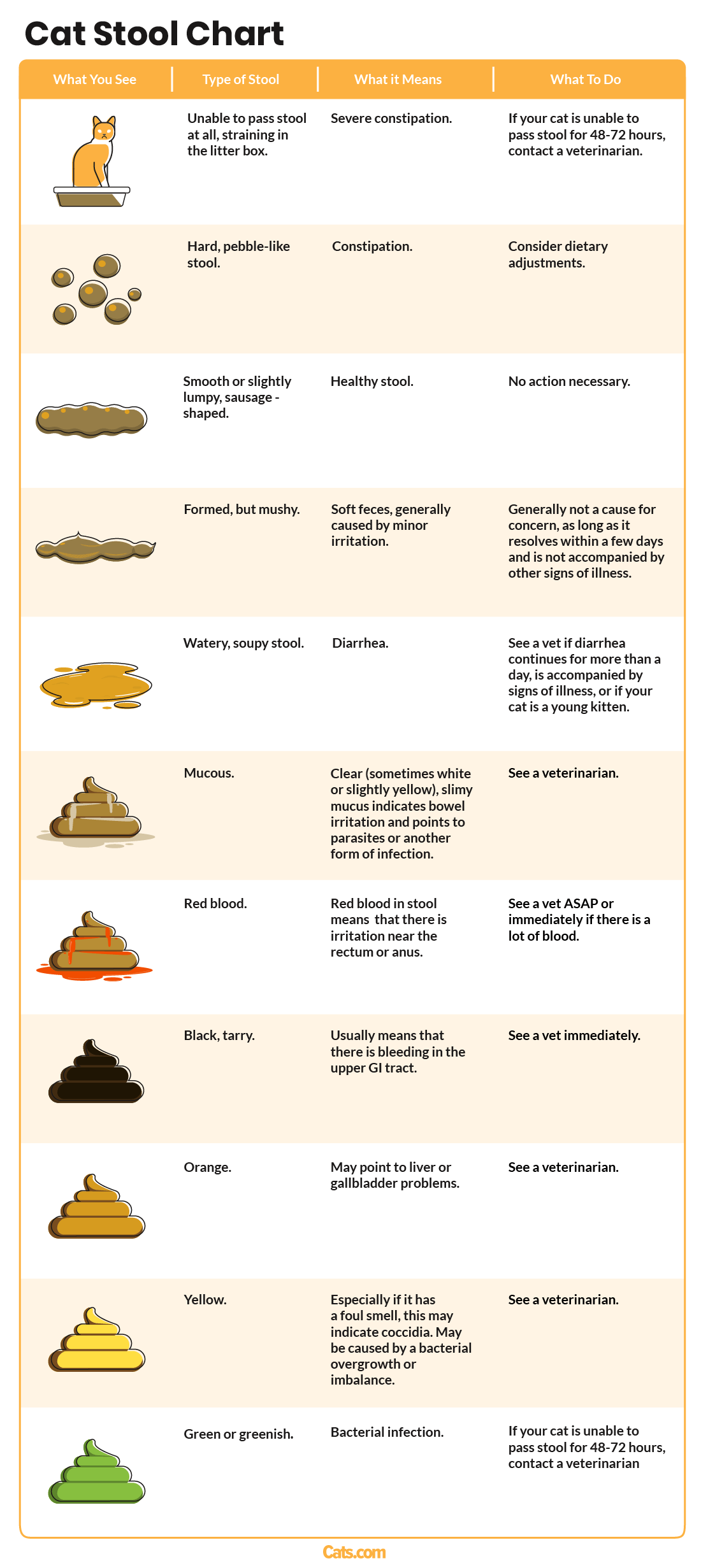
Breakdown Of Cat Stool Health Indicators Based On Color And Consistency

Fecal abnormalities may point to a wide variety of issues affecting the digestive tract and beyond.
It can be difficult to observe your cat’s bowel movements if they are outdoor pets, but if they use a litter box, you should take advantage of the daily task of scooping their poop to observe it in detail.
A normal cat stool should be brown or dark brown in color, with a reasonably firm consistency. The idea is that it should be formed, but should not be too hard.
There should be no sign of mucus or blood. It is possible to carry out “fecal scoring” based on a cat’s poop look, but there may be no need to get into such a detailed, formal way of carrying out an assessment.
Abnormalities that should be noted include:
- Extraneous matter, like hairballs.
Soft feces (formed, but mushy) can be caused simply by a sudden change of diet (e.g. from Purina to a different brand). Other possible causes include mild or early cases of diseases listed below that can cause more significant diarrhea. - Loose feces (diarrhea) can be caused by a number of factors, including intestinal irritation (e.g. by intestinal parasites such as tapeworm), bacterial infections, liver disease, kidney disease, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), food allergy, and food intolerances. Some health problems, like hyperthyroidism, can cause this type of diarrhea as well as a range of other signs of illness.
Broadly, There Are Two Sub-types Of Cat Diarrhea

First, small intestinal diarrhea tends to be larger pools of loose feces, passed less frequently. If blood is present, it may be darker, sometimes described as “tarry” (because it has been digested as it has passed through the digestive tract).
Second, large intestinal diarrhea (e.g. associated with colitis) tends to be smaller amounts of loose feces, passed more frequently, often with a sense of urgency. Streaks of mucus and fresh blood may be seen.
Read More: Best Cat Food for Diarrhea
Hard stool is the opposite of diarrhea, and this can indicate a range of other possible problems, You should also note the process of defecation: if your cat is straining when pooping (so-called “fecal tenesmus”) this can indicate constipation (e.g. megacolon or a blockage of some kind) or alternatively, this can be caused by irritation of the lower bowel.
You may notice your cat over-grooming around the same time as passing feces: this can suggest discomfort or abdominal pain.