
Intestinal parasites, some of which are commonly referred to as “worms,” are unfortunately all too common in pet cats. These parasites live inside your cat’s body, where they can wreak havoc on your cat’s health.
You might not know that your cat has intestinal parasites unless you see telltale signs (more about that below) or if your cat is heavily infested and begins to display physical symptoms of the infestation.
Veterinarians at Cornell University estimate that up to 45% of cats may be infected with intestinal parasites. The most common intestinal parasites that infect cats are roundworms, hookworms, tapeworms, coccidia, and Giardia.
How Do Cats Get Intestinal Parasites?
Cats can become infected by intestinal parasites in several different ways, depending on the specific parasite and the age of the cat. Cats most at risk are kittens, cats that go outdoors, or cats coming from places where large numbers of cats are housed together, like animal shelters, pet stores, or breeding catteries.
Kittens often get infected from their mother during nursing because some worms can be passed from mama cat to the kittens through the mother’s milk. It’s very common for kittens to be infected with worms. Starting at two weeks of age, kittens are dewormed every two weeks until they are about three months old. From 3 to 6 months of age, kittens are dewormed once a month.
Adult cats and kittens can also be infected with intestinal parasites by sharing food and water bowls or litter boxes with infected cats, eating rodents (roundworms or tapeworms), ingesting feces or contaminated soil or plant material (roundworms, hookworms, coccidia, or Giardia), walking across contaminated feces or soil (hookworms), or swallowing a flea (tapeworms).
What Kinds of Intestinal Parasites Do Cats Get?
Cats can get many different internal parasites. Some of the most common intestinal parasites seen in pet cats include:
Roundworms
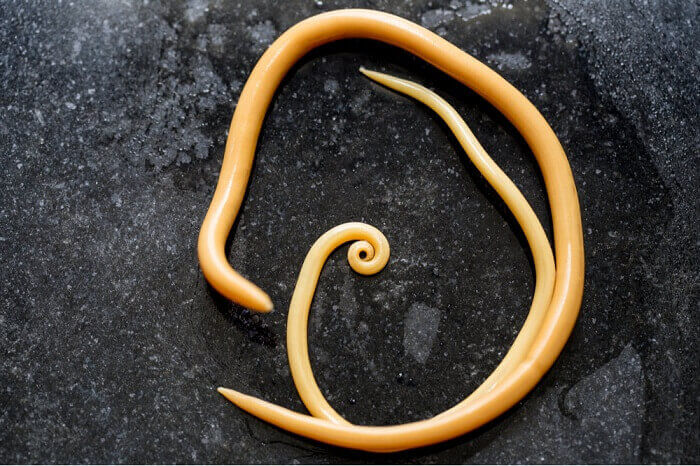

Roundworms (Toxocara cati and Toxascaris leonine) are the most common intestinal parasites in cats. Although any cat can become infected with roundworms, these worms are extremely common in kittens.
Kittens that are infected with roundworms frequently have a telltale potbelly (distended abdomen). Roundworms live in the intestines, where they feed on the food your cat eats. Over time, roundworm infestation can contribute to malnutrition. Roundworms can be transmitted to people.
Hookworms
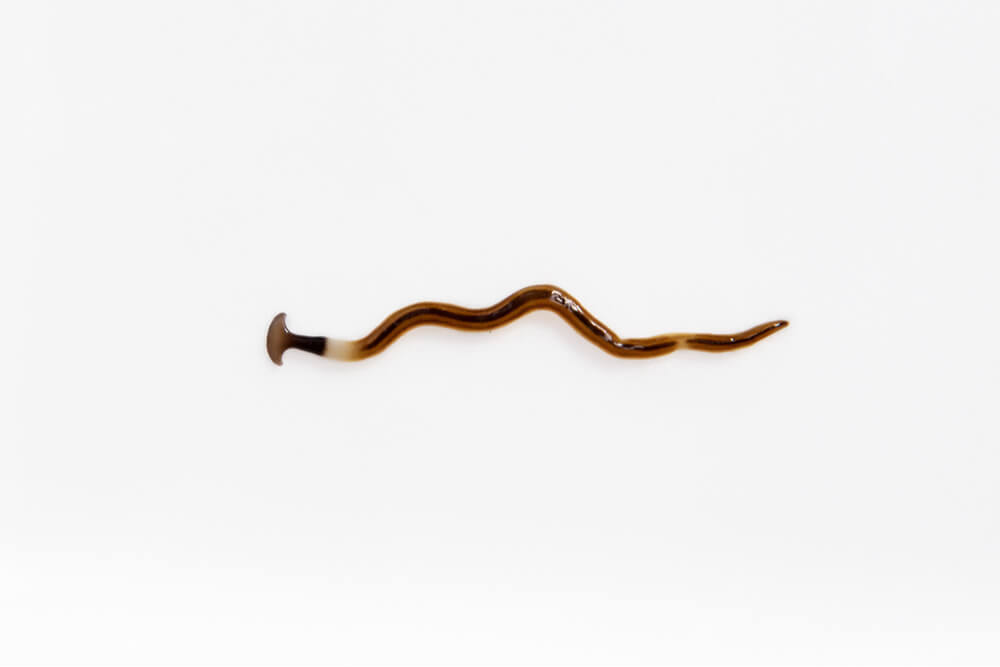

Hookworms are small worms that attach themselves to the lining of the intestines, where they feed on your cat’s blood. Severe hookworm infestations can cause anemia.
Cats become infected when they ingest hookworm larvae or walk on contaminated feces, cat litter, or soil. When a cat walks on a surface contaminated with hookworms, the larvae enter the body by penetrating the skin. Hookworms can be transmitted to people and other pets.
Tapeworms
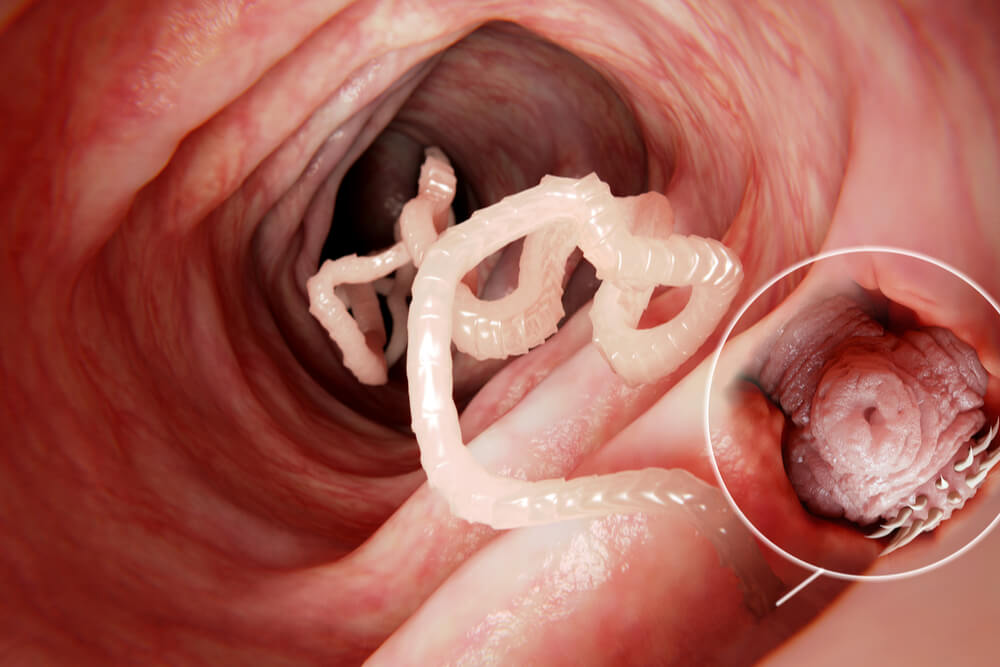
Cats or kittens commonly contract tapeworms when they swallow an infected flea during self-grooming. The flea acts as an intermediate host for the tapeworm. When the cat swallows it, the tapeworm eventually takes up residence in the cat’s intestines, where it attaches itself to the lining of the intestines with its hooked teeth.
Cats can also end up with tapeworms if they eat a mouse, rat, rabbit, or other small animal infected with tapeworms. Once inside a cat, tapeworms can grow to enormous lengths: up to 11 inches (30 centimeters).
Tapeworms are segmented. Tiny segments of the worm, called proglottids, can break off and pass out of the cat’s body in the stool. These segments are visible to the naked eyes and look like white or yellowish grains of rice.
Coccidia
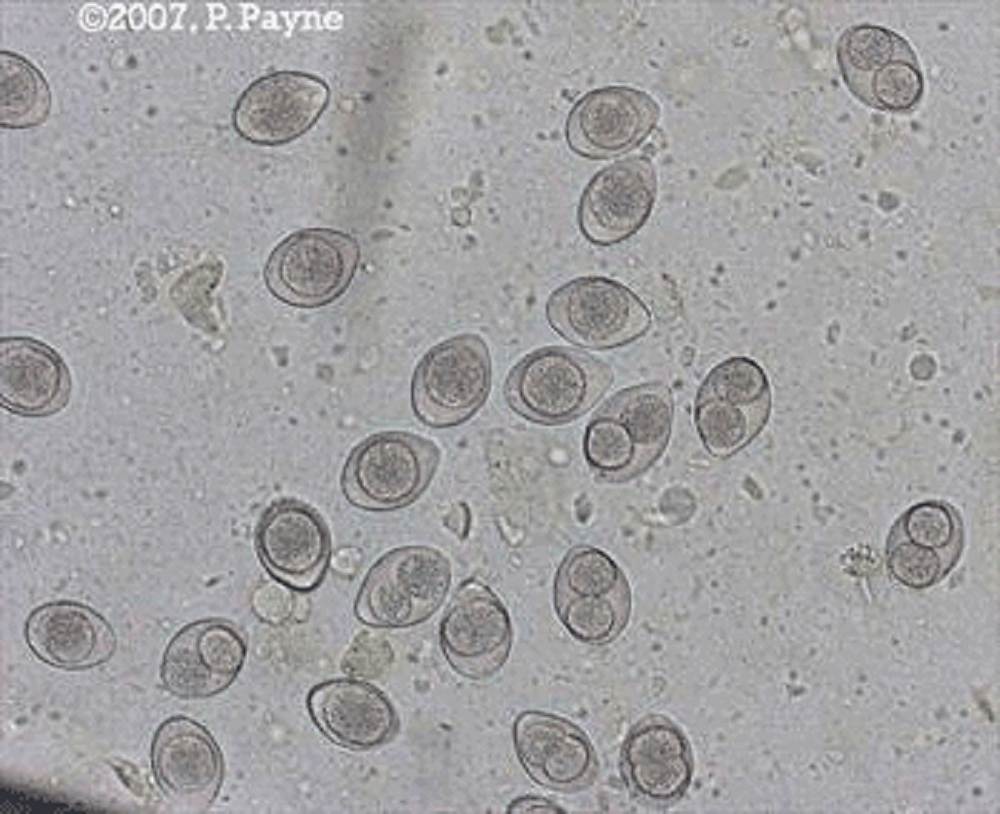
Image from urbananimalveterinary.com
Coccidiosis is caused by coccidia (Isospora felis, Isospora rivolta), microscopic single-celled parasites that live in a cat’s intestinal wall. Cats become infected when they ingest an infected cat’s feces or soil that has been contaminated with feces. Coccidia causes severe diarrhea, which can be life-threatening in young kittens.
Giardia
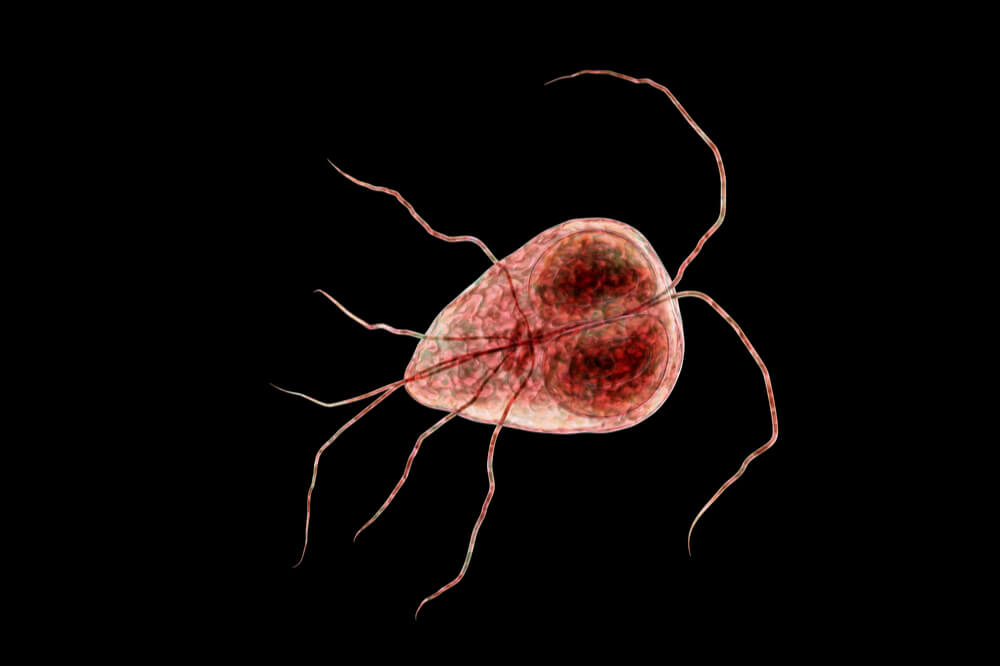
Giardia infection, called giardiasis, is caused by tiny single-celled protozoan parasites (Giardia duodenalis) that live in the intestines and cause diarrhea. Kittens are most at risk, along with senior cats, immunocompromised cats, and cats that are ill. Cats become infected with Giardia if they ingest the feces of another infected cat. It’s possible that cats can pass Giardia infection to humans.
Symptoms of Cat Worms

The symptoms of cat worms can be subtle, sometimes only becoming apparent during a routine fecal examination. Other symptoms include anemia, bloating, digestive symptoms, and signs of malnutrition.
You may see no symptoms that your cat has intestinal parasites, even if they’re causing problems with your cat’s health.
This is why veterinarians recommend routine fecal exams (called fecal flotation tests) once or twice a year to check the stool for worm eggs or cysts from protozoa (single-celled organisms). If you can, provide your vet with a fresh stool sample from your cat when it’s time for a fecal exam.
If your cat is heavily infested, you might notice signs that your cat has intestinal parasites.
Symptoms of worms include:
- Anemia
- Bloated belly (potbelly)
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Gas
- Lethargy (lack of energy)
- Licking or biting under the tail
- Loss of appetite
- Malnutrition
- Restricted growth
- Scooting (dragging the rear on the floor)
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment for intestinal parasites is with medications called anthelmintics, which kill intestinal worms and other intestinal parasites. Although some anthelmintics are available over the counter without a prescription, different anthelmintics kill different intestinal parasites, so it’s important to find out first what type of parasites your cat has. Additionally, some parasites require prescription medications that are only available from your vet.
To find out what type of intestinal parasites your cat has, your veterinarian will conduct a fecal exam.
After collecting a sample of your cat’s stool (or you provide a fresh stool sample), the veterinarian will examine it under a microscope. The vet is not searching for adult worms, but instead is looking for the presence of worm eggs, Giardia cysts, or oocysts (immature coccidia). Once these have been found, the vet can identify which intestinal parasites are infecting your cat.
Cats can be infected with more than one type of intestinal parasite at the same time. Sometimes, the same medication will kill all the parasites; other times, your cat might need more than one anthelmintic.
If you have other cats in the home, your veterinarian might recommend that you treat all the cats in the house for intestinal parasites.
If your cat has tapeworms, the treatment is two-part. First, your veterinarian will prescribe a medication to kill the tapeworms your cat has. Second, your cat and your home should be treated for fleas. Flea infestation and tapeworms go hand in hand because cats get tapeworms by ingesting a flea.
If the cat has fleas or if you have fleas or flea eggs in your home, the cat will continue to become re-infected with tapeworms.
Your veterinarian can recommend an oral or topical flea control product to kill the fleas on the cat. Additionally, you should treat your home and yard for fleas, either using a commercially available flea product or by consulting with a professional exterminator.
Also Read: Best Cat Dewormers
Preventing Cat Intestinal Parasites
When it comes to intestinal parasites, prevention is the best medicine. Certain monthly flea, tick, and heartworm preventives also protect your cat against certain intestinal parasites (commonly roundworms and hookworms). Talk to your veterinarian about the best parasite prevention for your cat.
Whichever preventative you choose, use it year-round and follow the instructions carefully.







